- info@bioicawtech.com
- Helsinki, Finland
- Request a quote
Drug repurposing
-
BioICAWTech > Drug repurposing
Drug repurposing catalogue
We have extensive experience in developing in-silico methods for drug repurposing. Survey of 178 in-silico resources in terms of their added value for a wide range of drug repurposing applications.
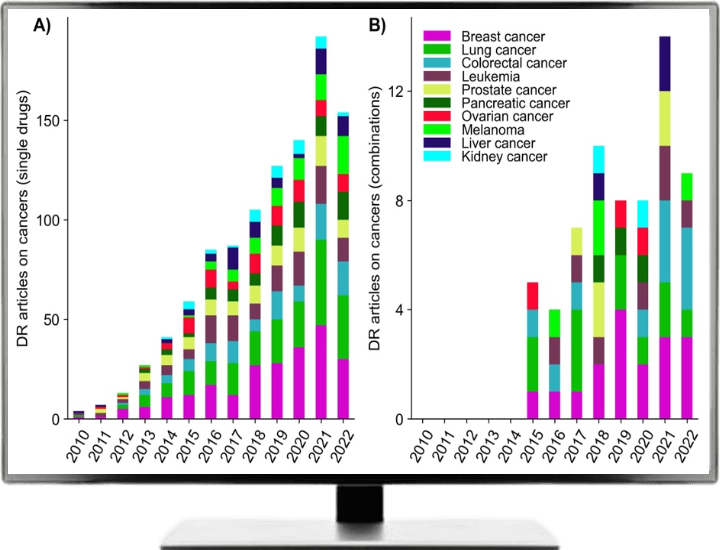
Since 2010, number of published articles related to single drug or combination-based drug repurposing shown an increasing trend especially for the ten cancer types as shown in following Figure.
Therefore, scientists at our company have started developing new ways of drug repurposing by carefully exploring pros and cons of existing available methods and tools. Our scientists have been the primary authors in four drug-repurposing related survey articles.
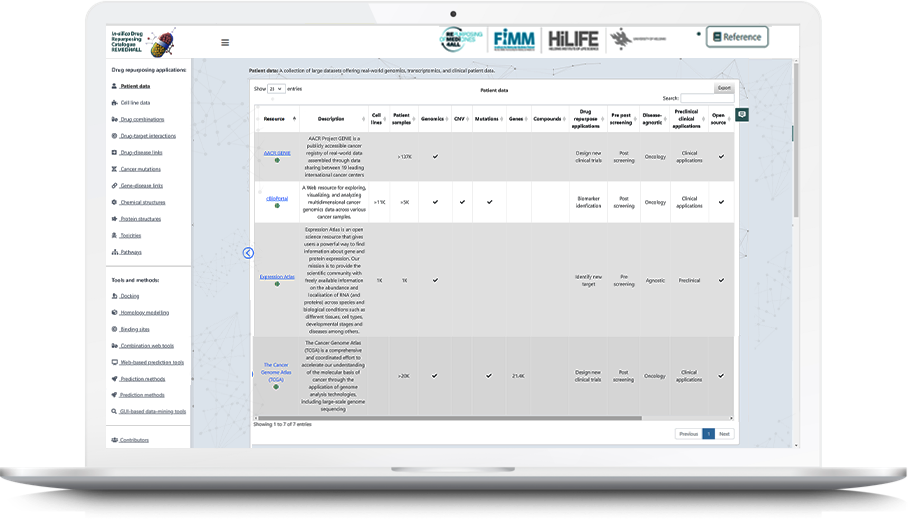
We have analyzed data from dozens of publicly available chemical and biological databases related to several categories, e.g. drug-target interactions, drug sensitivities, adverse drug reactions, protein structures, chemical structures, clinical databases, disease-genes associations, and drug combinations, etc. In our latest review article (currently under review in Nature Reviews Drug Discovery), we defined a novel ontology to classify and annotate 178 drug repurposing tools/methods into 15 sub categories of drug repurposing also shown in our database: https://idrc-r4a.com/ and summarized in following Figure.
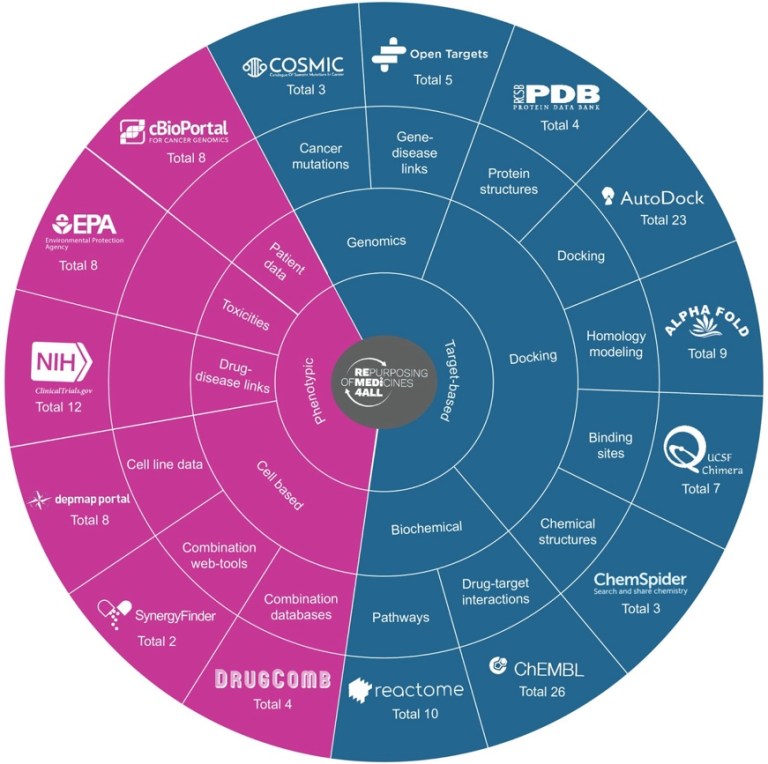
In this drug-repurposing review, we have efficiently collaborated with 43 different scientists from 23 institutes and pharma companies within European Union.
We plan to expand this catalogue (https://idrc-r4a.com/) to make it an encyclopedia for up-to-date information about newly developed as well as existing drug-repurposing related tools, databases and methods.
